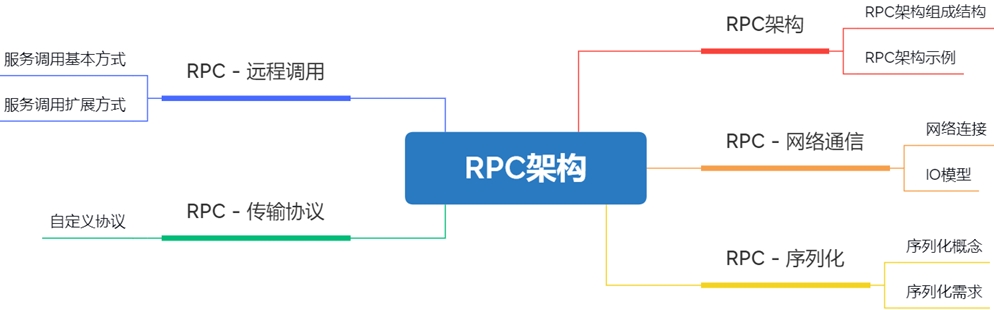
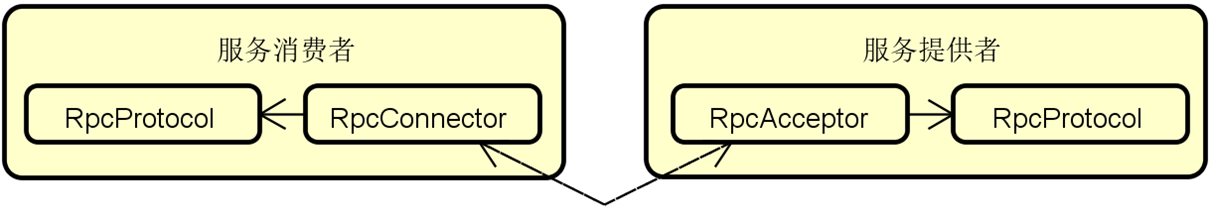
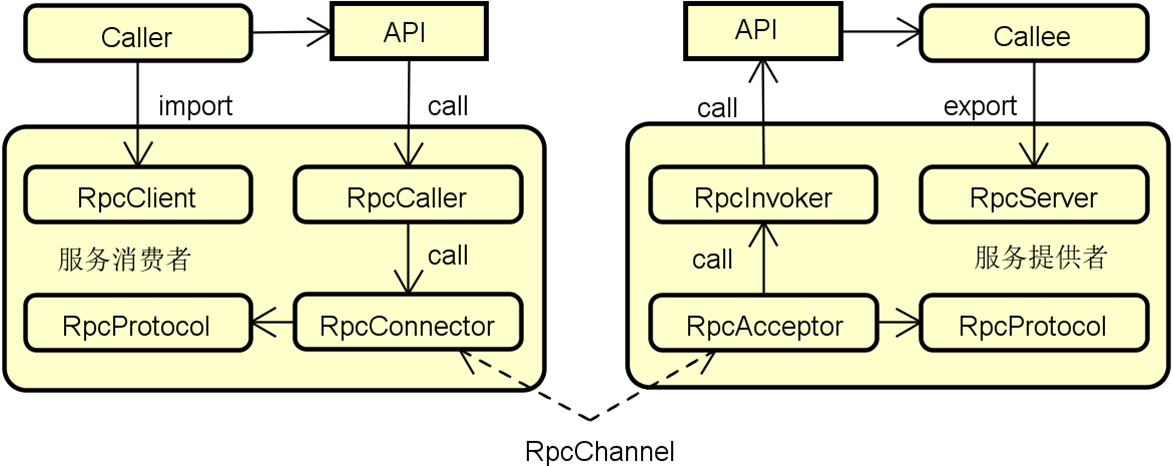
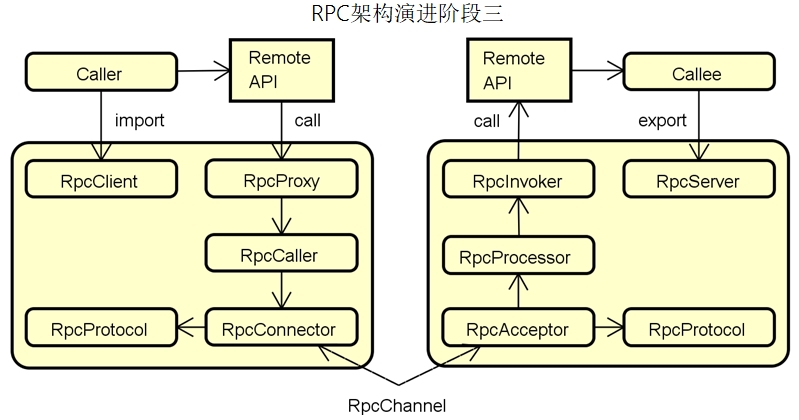
RPC架构的基本结构
核心组件
网络通信
传输协议
远程调用
序列化
RPC架构基本结构 Remote Process Call远程过程调用
架构演进
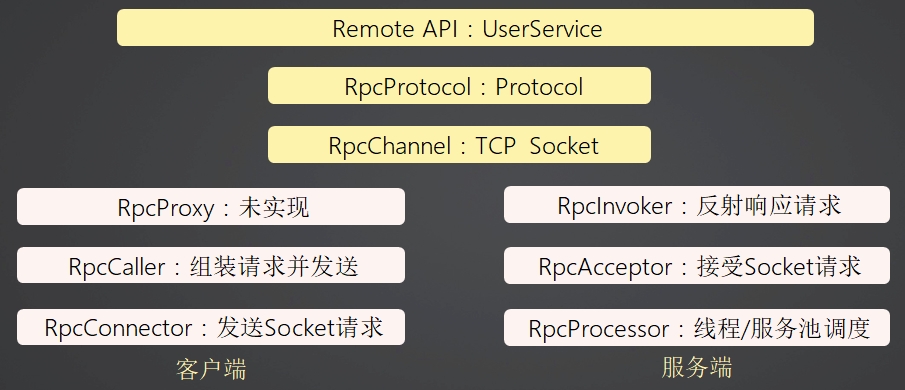
客户端组件-职责
服务端组件-职责
通用组件-职责
示例-自定义RPC架构
Protocol 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 package com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.protocol; import java.io.Serializable; public class Protocl implements Serializable { private String interfaceName; String methodName; Class[]paramsTypes; Object[]parameters; public Protocl() { super(); } public Protocl(String interfaceName, String methodName, Class[] paramsTypes, Object[] parameters) { this.interfaceName = interfaceName; this.methodName = methodName; this.paramsTypes = paramsTypes; this.parameters = parameters; } public String getInterfaceName() { return interfaceName; } public void setInterfaceName(String interfaceName) { this.interfaceName = interfaceName; } public String getMethodName() { return methodName; } public void setMethodName(String methodName) { this.methodName = methodName; } public Class[] getParamsTypes() { return paramsTypes; } public void setParamsTypes(Class[] paramsTypes) { this.paramsTypes = paramsTypes; } public Object[] getParameters() { return parameters; } public void setParameters(Object[] parameters) { this.parameters = parameters; } }
API 1 2 3 public interface UserService { public String getUserNameByCode(String userCode); }
Server 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 package com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.server; import com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.protocol.Protocl; import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.TypeReference; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import javax.naming.ldap.SortKey; import java.io.IOError; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class RpcServer { private int threadSize = 10; private ExecutorService threadPool; private Map<String, Object> servicePool; private int port = 9901; public int getThreadSize() { return threadSize; } public void setThreadSize(int threadSize) { this.threadSize = threadSize; } public ExecutorService getThreadPool() { return threadPool; } public void setThreadPool(ExecutorService threadPool) { this.threadPool = threadPool; } public Map<String, Object> getServicePool() { return servicePool; } public void setServicePool(Map<String, Object> servicePool) { this.servicePool = servicePool; } public int getPort() { return port; } public void setPort(int port) { this.port = port; } public RpcServer() { super(); synchronized (this) { threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(this.threadSize); } } public RpcServer(int threadSize, int port) { this.threadSize = threadSize; this.port = port; synchronized (this) { threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(this.threadSize); } } public RpcServer(Map<String, Object> servicePool, int threadSize, int port) { this.threadSize = threadSize; this.port = port; this.servicePool = servicePool; synchronized (this) { threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(this.threadSize); } } /** * 1.实现Socket监听:RpcAcceptor * @throws IOException */ public void service() throws IOException { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(this.port); while (true) { Socket receiveSocket = serverSocket.accept(); final Socket socket = receiveSocket; //执行请求 threadPool.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { //处理请求 process(socket); socket.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } } /** *处理请求:RpcProcessor` */ private void process(Socket receiveSocke) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException { ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(receiveSocke.getInputStream()); Protocl transportMessage = (Protocl) objectInputStream.readObject(); //调用服务 Object result = call(transportMessage); ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(receiveSocke.getOutputStream()); objectOutputStream.writeObject(result); objectOutputStream.close(); } /** * 3.执行方法调用,RpcInvoker */ private Object call(Protocl protocl) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException { if (servicePool == null) { synchronized (this) { servicePool = new HashMap<>(); } } String interfaceName = protocl.getInterfaceName(); Object service = servicePool.get(interfaceName); Class<?> serviceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName); if (service == null) { synchronized (this) { service = serviceClass.newInstance(); servicePool.put(interfaceName, service); } } Method method = serviceClass.getMethod(protocl.getMethodName(), protocl.getParamsTypes()); Object result = method.invoke(service, protocl.getParameters()); return result; } }
serviceImpl 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 package com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.service.impl; import com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.service.UserService; public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Override public String getUserNameByCode(String userCode) { return "hello:" + userCode; } }
Client 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.client; import com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.protocol.Protocl; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.net.Socket; import java.net.UnknownHostException; public class RpcClient { private String serverAddress; private int serverPort; public RpcClient(String serverAddress, int serverPort) { this.serverAddress = serverAddress; this.serverPort = serverPort; } public Object sendAndRecevie(Protocl protocl) { Object result = null; try { Socket socket = new Socket(this.serverAddress, this.serverPort); ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); objectOutputStream.writeObject(protocl); ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); result = objectInputStream.readObject(); } catch (UnknownHostException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return result; } }
测试 Server 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package com.vvf.rpc.server; import com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.server.RpcServer; import com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.service.impl.UserServiceImpl; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class ServerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, Object> servicePool = new HashMap<>(); servicePool.put("com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.service.UserService", new UserServiceImpl()); RpcServer server = new RpcServer(servicePool, 4, 9001); try { server.service(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Client 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package com.vvf.rpc.client; import com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.client.RpcClient; import com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.protocol.Protocl; public class ClientTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String serverAddress = "127.0.0.1"; int serverPort = 9001; RpcClient client = new RpcClient(serverAddress, serverPort); Object result = client.sendAndRecevie(buildProtocol("vvf1")); System.out.println(result); } private static Protocl buildProtocol(String userCode) { String interfaceName = "com.vvf.springboot1.demos.rpc.service.UserService"; Class[] paramsTypes = {String.class}; Object[] parameters = {userCode}; String methodName = "getUserNameByCode"; Protocl transportMessage = new Protocl(interfaceName, methodName, paramsTypes, parameters); return transportMessage; } }
核心组件-网络通信 网络连接
长连接
短连接
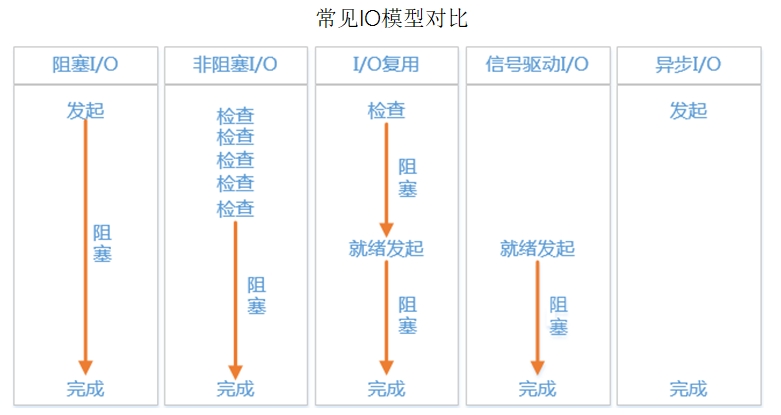
IO模型
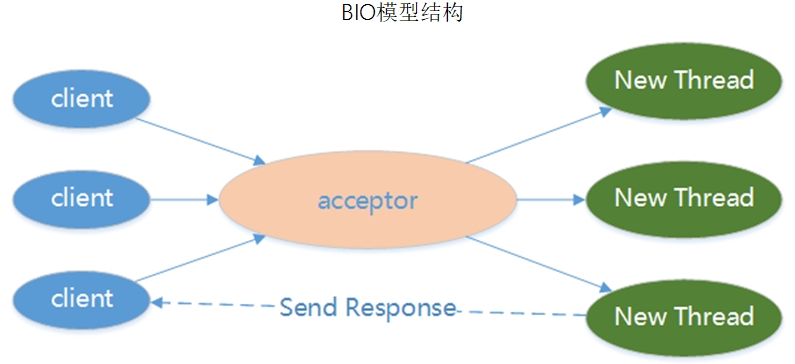
bio
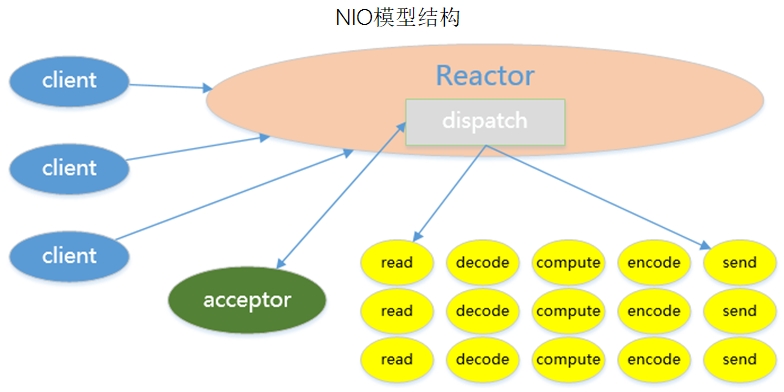
nio
I/O多路复用
信号驱动I/O
异步I/O aio
阻塞I/O bio 单线程只能同时处理一个链接,(客户端断开才能处理下一个,全流程阻塞)
非阻塞I/O nio 接收请求时不阻塞,执行时阻塞
单线程保持多链接,但数据从内核缓冲区拷贝到用户态时阻塞。read就是将内核缓冲区就绪数据读取到用户态。 网卡将数据拷贝到内核缓冲区时,发出系统中断命令,修改socket文件描述符为就绪态,read此时阻塞读取数据
I/O多路复用 selector多路复用器
信号驱动I/O 异步I/O aio 非阻塞
对比
NIO模型依赖于操作系统的I/O多路复用技术,如select、poll、epoll模型
问题:NIO BIO AIO区别?select、poll、epoll区别?
为什么选择linux系统?
核心组件-序列化· 序列化:对象 -> 字节数组(用于网络传输,持久化等)
方式
文本类
二进制类
跨语言 常见的跨语言支持序列化工具:Hession、Protocol Buffer、Thrift、Avro
支持数据结构种类
接口开发友好性
性能
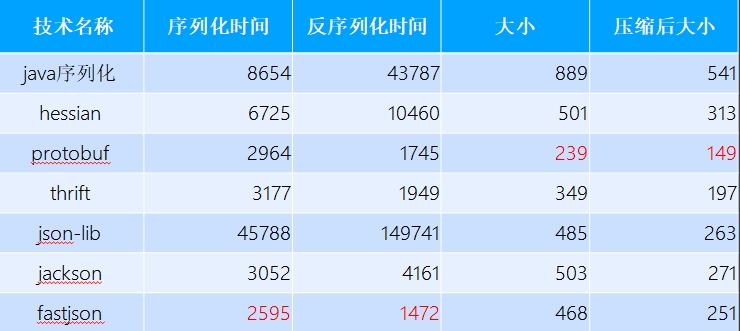
java序列化工具对比:https://github.com/eishay/jvm-serializers
核心组件-传输协议
自定义协议 性能与扩展性
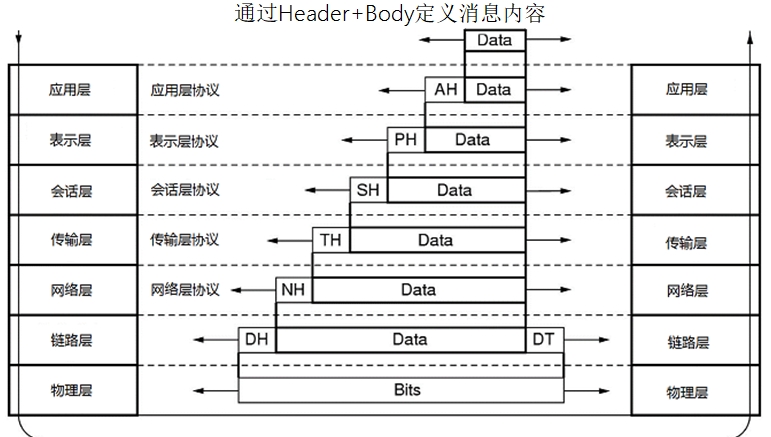
自定义协议的通信模型和消息定义(自定义传输对象消息头消息体)
支持点对点长连接通信
使用NIO模型进行异步通信
提供可扩展的编解码框架,支持多种序列化方式
在已有协议基础上做扩展
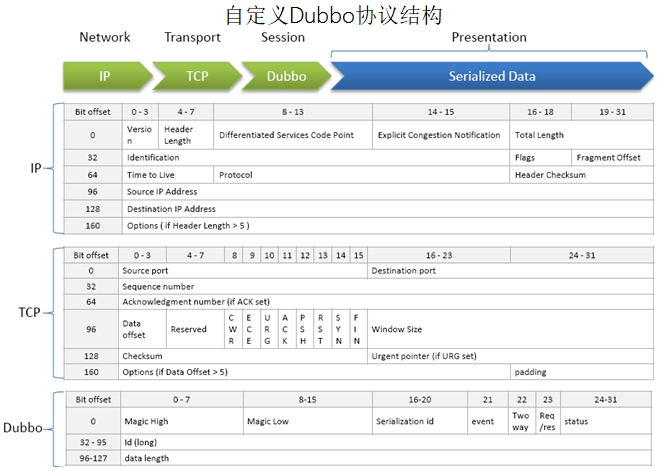
Dubbo协议
核心组件-远程调用 服务调用基本方式
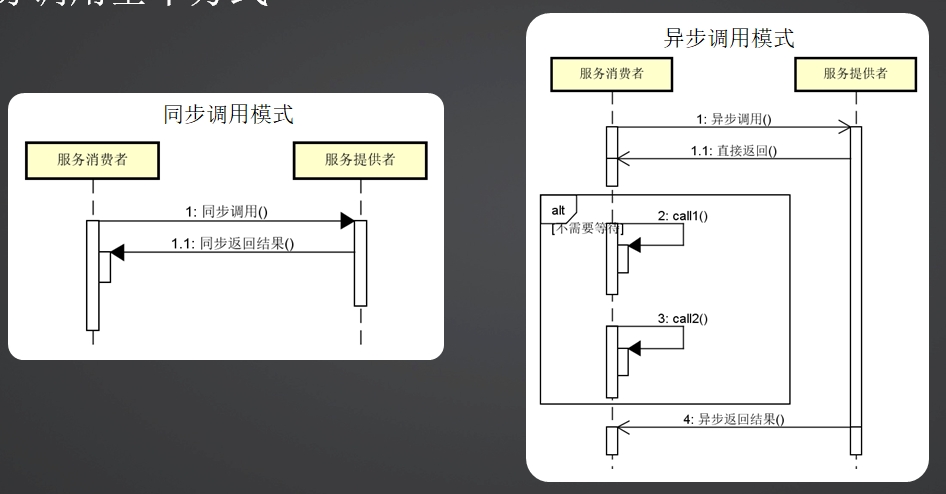
同步
异步
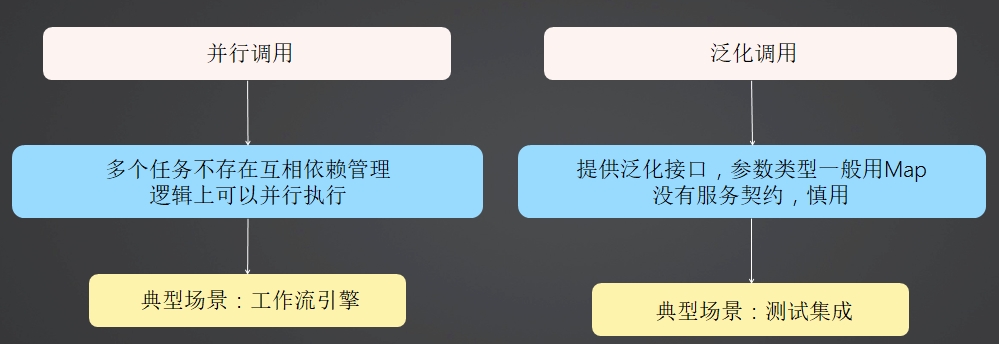
并行调用
泛化调用