markword:不同虚拟机实现不同,hospot是对象头的两位(不同组合对应不同类型的锁)
锁升级
锁特性 synchronize(this)
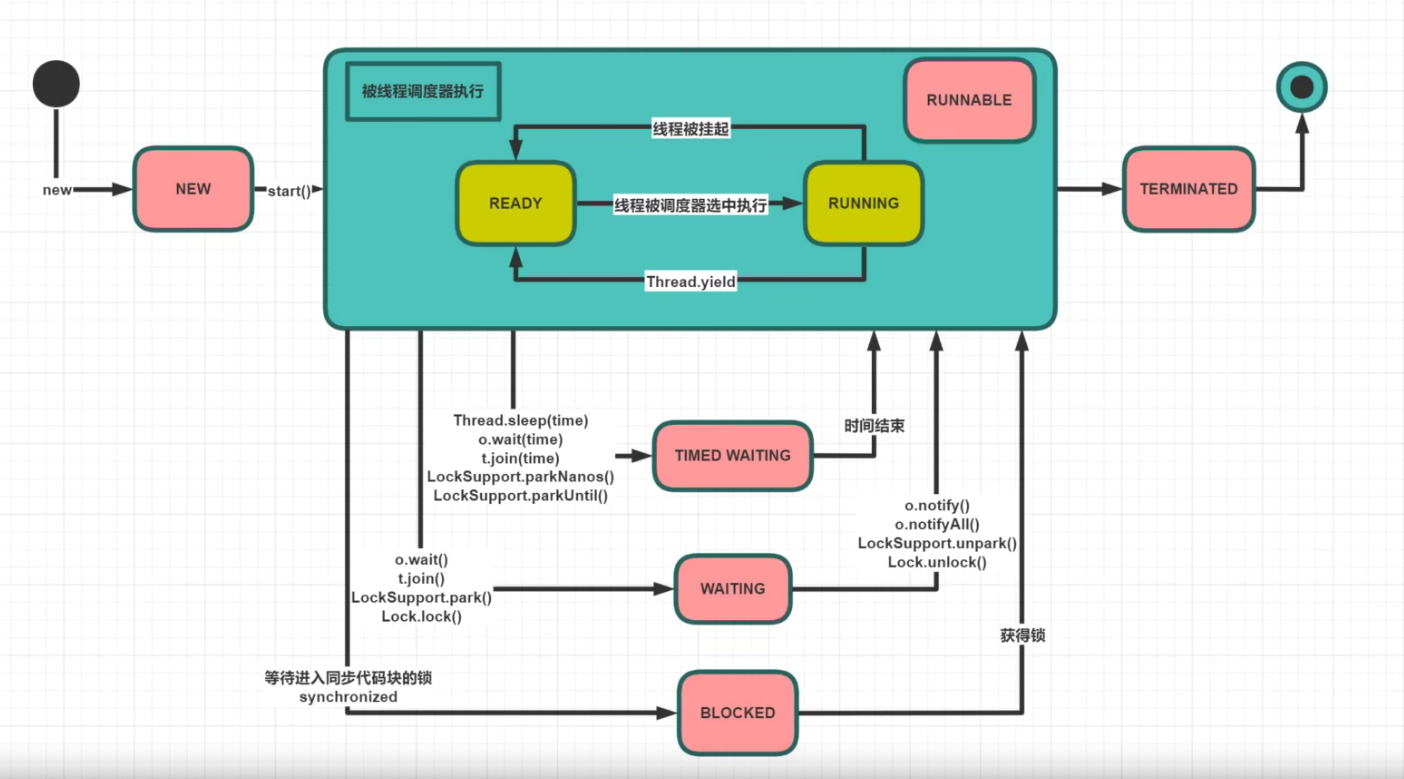
线程的基本方法 sleep 线程暂停执行,到时自动唤醒,进入就绪态
创建线程对象
启动线程的方式
runnable
thread
线程池(也是使用前两种启动线程)
线程状态
CAS无锁优化 自旋 相关类所在包:package java.util.concurrent.atomic
Compare and swap 说明:1 2 3 cas(v,expected,newValue) if v==expected set v=newValue else fail
ABA问题 数值类型不会引发ABA问题,引用类型才有AtomicStampedReference
synchronized 底层实现(hospot)
早期jdk实现是重量级的(向操作系统申请锁)
优化后:(锁升级)
自旋锁,重量级锁应用场景 自旋锁:占用CPU,不访问操作系统内核(线程数少,锁代码块执行时间短)
synchronized异常锁 默认,异常后自动释放锁。若数据一致性处理不好,会导致其他线程获取到中间数据(脏数据)。
synchronized优化
粒度
细粒度锁,尽量不锁住不需要锁的代码
粗粒度锁,一段代码加多个细粒度锁时效率也不高(例如数据库行锁,表锁)
锁对象不应发生改变
unsafe类 volatile
保证线程可见性
禁止指令重排(CPU)
不保证原子性
线程可见性代码测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class TestVolatile { boolean flag = true; AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0); public void test1() throws InterruptedException { Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("t1 start"); while (flag) { //不能使用println //不能使用sleep } System.out.println("t1 end"); }); Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { try { System.out.println("t2 start sleep 3s"); Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("t2 wakeup and set flag false"); flag = false; }); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
问题 测试代码中test1方法的循环体内不可使用println和sleep
不能使用println,println是线程安全代码,synchronized加锁会重新读取内存中的值
线程解锁前,必须把共享变量的最新值刷新到主内存中;
线程加锁时,先清空工作内存中共享变量的值,从而使用共享变量是需要从主内存中重新读取最新的值(加锁与解锁需要统一把锁)
不能使用sleep(暂不清楚原因??????)
禁止指令重排DCL应用说明 赋值操作分为三个步骤 {1}堆申请空间 {2}初始化字段值 {3}返回地址给变量
CountDownLatch 门栓,实例化对象时声明门栓数
比join更灵活
CyclicBarrier 满员发车
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class CustomCyclicBarrier { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CustomCyclicBarrier customCyclicBarrier = new CustomCyclicBarrier(); CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(10, customCyclicBarrier::showSomething); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { int finalI = i; new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(finalI + " running"); try { barrier.await(); System.out.println(finalI + "free"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }).start(); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("thread started:" + i); } } public void showSomething() { System.out.println("ok"); } }
LongAdder 解决问题:解决atomic* 并发量越大时,cas失败率越高,cpu空转,性能差
phaser 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 public static void main(String[] args) { Phaser phaser = new CustomPhaser(); Random r = new Random(); phaser.bulkRegister(7); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { new Thread(new Person("person" + i, phaser, r)).start(); } new Thread(new Person("新郎", phaser, r)).start(); new Thread(new Person("新娘", phaser, r)).start(); } public class Person implements Runnable { String name; Phaser phaser; Random r; int sleepSec = 3; public Person(String name, Phaser phaser, Random random) { this.name = name; this.phaser = phaser; random = r; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { arrive(); eat(); leave(); hug(); } public void arrive() { this.sleep(sleepSec); System.out.printf("%s 到达\n", this.name); this.phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); System.out.println("开始吃饭+" + this.name); } public void eat() { this.sleep(sleepSec); System.out.printf("%s 吃完了\n", this.name); this.phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); } public void leave() { if (this.name != "新郎" && this.name != "新娘") { this.sleep(sleepSec); System.out.printf("%s 离开\r\n", this.name); this.phaser.arriveAndDeregister(); } else { this.phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); } } public void hug() { if (this.name == "新郎" || this.name == "新娘") { this.sleep(sleepSec); System.out.printf("%s 抱抱\n", this.name); this.phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance(); } else { this.phaser.arriveAndDeregister(); } } public void sleep(int millSeconds) { try { Thread.sleep(millSeconds); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public void sleepRandom(int seconds) { sleep(r.nextInt(1000) * seconds); } } public class CustomPhaser extends Phaser { @Override protected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) { switch (phase) { case 0: System.out.println("------都到齐了" + registeredParties); System.out.println(); return false; case 1: System.out.println("------都吃完了" + registeredParties); System.out.println(); return false; case 2: System.out.println("------都离开了" + registeredParties); System.out.println(); return false; case 3: System.out.println("------婚礼结束" + registeredParties); return true; default: return true; } } }
ReadWriteLock 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class CustomReadAndWriteLock { public static void main(String[] args) { ReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); Runnable read = () -> { try { lock.readLock().lock(); System.out.println("reading"); Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { lock.readLock().unlock(); System.out.println("read end"); } }; Runnable write = () -> { try { lock.writeLock().lock(); System.out.println("writing"); Thread.sleep(5 * 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { lock.writeLock().unlock(); System.out.println("write end"); } }; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(read).start(); } for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { new Thread(write).start(); } } }
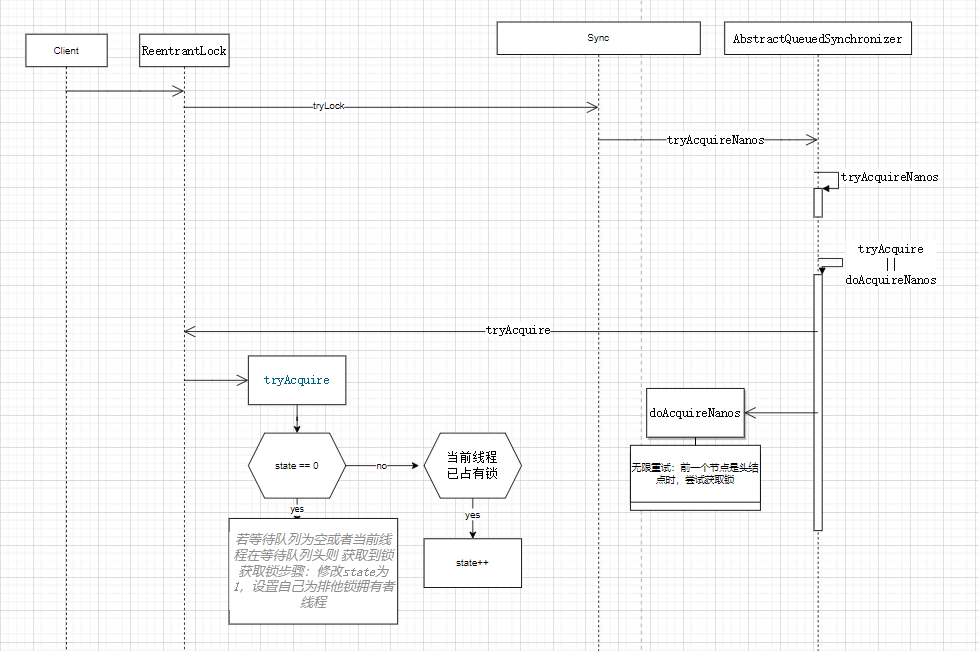
ReentranLock 实现是一种自旋锁CAS
condition,本质时创建多个等待队列,可唤醒指定等待队列中的线程(notifyAll唤醒所有等待队列中的线程)
trylock 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); try { if (lock.tryLock(1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) { //do something } }finally { lock.unlock(); }
lockInterruptibly 响应打断
公平锁 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
Semaphore 限流,最多允许多少个线程同时运行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class TestSemaphore { public static void main(String[] args) { Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(5); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { int finalI = i; new Thread(() -> { try { semaphore.acquire(); System.out.println("acquire:" + finalI); Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { semaphore.release(); } }).start(); } } }
Exchanger 两个线程交换数据,第一个调用exchange方法时阻塞,第二个线程调用exchange方法时交换数据后继续执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class TestExchange { public static void main(String[] args) { Exchanger<String> exchanger = new Exchanger<>(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); String s = String.valueOf(i); System.out.println("thread-1-org:" + s); s = exchanger.exchange(s); System.out.println("thread-1-exchanged:" + s); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }).start(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 100; i > 97; i--) { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); String s = String.valueOf(i); System.out.println("thread-2-org:" + s); s = exchanger.exchange(s); System.out.println("thread-2-exchanged:" + s); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }).start(); } }
LockSuport 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class TestLockSupport { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread t = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println(i); if (i == 4) { System.out.println("t park1"); LockSupport.park(); } else if (i == 8) { System.out.println("t park2"); LockSupport.park(); } try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }); t.start(); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(6); System.out.println("unpark"); LockSupport.unpark(t); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);// park之前就执行unpark也是可以的 System.out.println("unpark"); LockSupport.unpark(t); } }
线程interrupt打断 优雅终止线程方法之一
三个方法 interrupt 设置标志位,线程根据标志位自己决定怎么做
interrupt与sleep、wait、join 线程在sleep 、wait、join时设置其打断标志位线程会中断并抛出异常InterruptedException
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public class TestInterrupt { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new TestInterrupt().testWaitInterrupted(); } public void testSleepInterrupted() throws InterruptedException { Thread t = new Thread(() -> { while (true) { try { Thread.sleep(500); System.out.println("running"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("InterruptedException"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); //输出false 异常后自动重置标志位 break; } if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { break; } } },"t"); t.start(); Thread.sleep(2000); t.interrupt(); } public void testWaitInterrupted() throws InterruptedException { Thread t = new Thread(() -> { synchronized (this) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("InterruptedException"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); } } }); t.start(); Thread.sleep(2000); t.interrupt(); } }
interrupt与synchronized 线程在等待锁时设置其标志位不会抛出异常
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public void testSync() throws InterruptedException { Thread t = new Thread(() -> { synchronized (this) { System.out.println("t1 locked"); try { Thread.sleep(10 * 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } System.out.println("t1 end"); }); t.start(); Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { synchronized (this) { System.out.println("t2 locked"); } System.out.println("t2 end"); }); t2.start(); t2.interrupt(); }
interrupt与ReentranLock 使用ReentranLock.lock阻塞等待获取锁时也不会被打断 ,使用lock.lookInterruptibly()获取锁可以被打断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public void testReentrantLock() throws InterruptedException { ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Thread t = new Thread(() -> { try { lock.lock(); System.out.println("t1 locked"); try { Thread.sleep(6 * 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } System.out.println("t1 end"); }); t.start(); Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { try { lock.lockInterruptibly(); System.out.println("t2 locked"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { lock.unlock(); } System.out.println("t2 end"); }); t2.start(); Thread.sleep(2000); t2.interrupt(); }
线程结束 stop(不建议) 不建议用stop,粗暴结束,容易产生数据不一致(释放锁,不做善后处理)
interrupt volatile flag :特定场景优雅(不是很精确)
遇到sleep、wait时等待不能执行循环,不能判断标志位,不能立即结束
打断时间不精确,如阻塞容器,容量为5时结束,但由于volatile同步线程标志位时间控制不是很精确,有时会延迟一会儿
interrupt :
sleep、wait场景下可以结束
精确结束:业务线程和触发结束的线程配合
AQS(CLH) 基础框架,广泛应用于实现锁和其他同步器(如ReentrantLock、CountDownLatch、Semaphore等)
state volatile修饰 保证线程可见
线程链表 链表中的线程争用state(取锁)
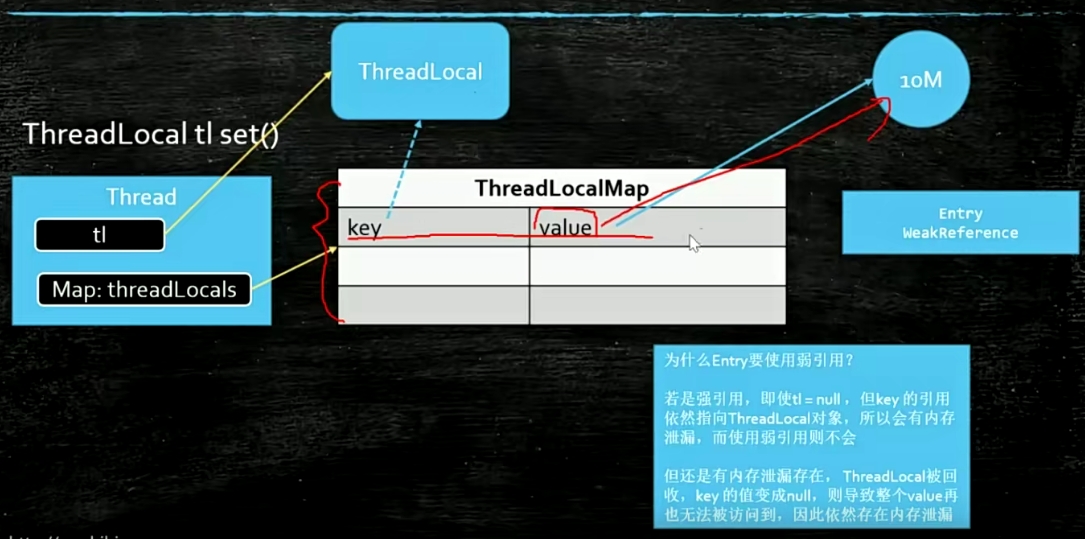
ThreadLocal 每个线程都有自己独有map
强软弱虚四种引用 软引用 SoftReference 垃圾回收时不会立刻回收,内存不足时回收 ;用于缓存
弱引用 WeakReference 垃圾回收就会回收 ; 另外一个强引用引用它时,强引用消失,弱引用就被回收。(WeakHashmap)
虚引用 JVM开发用来管理堆外内存。PhantomReference<myM> saf = new PhantomReference<>(new myM(), queue1)
源码 阅读原则
了解骨架
跑不起来不读(很困难)
有目的性,理解别人的思路
一条线索到底
略过无关细节
一般不读静态
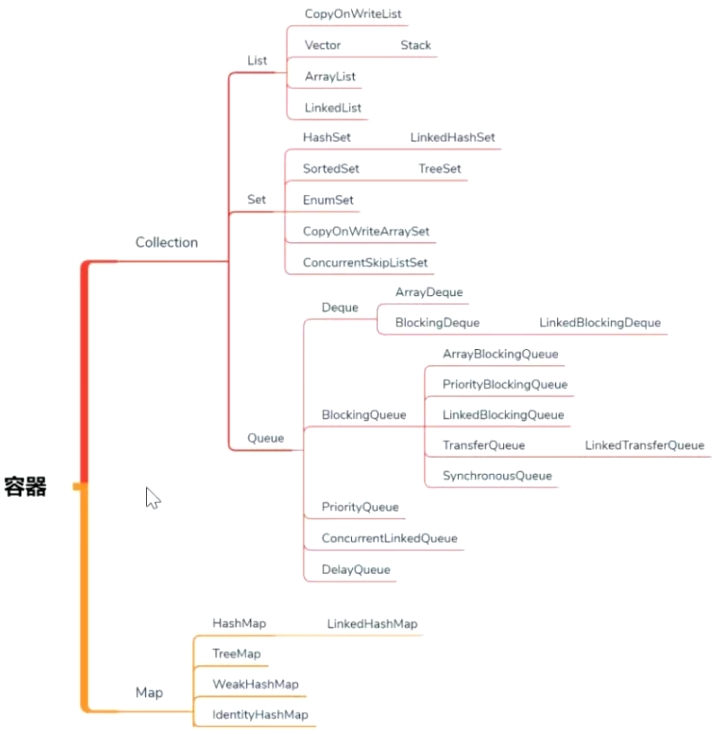
容器
Vector/Hashtable 自带锁Hashtable -> Hashmap -> SynchronizedMap[Collections.synchronizedMap()] -> ConcurrentHashMap
Hashtable发展历程
Hashtable 全部接口自带锁
Hashmap 无锁(现成不安全)
SynchronizedMap 满足Hashmap某些场景需要加锁
ConcurrentHashMap
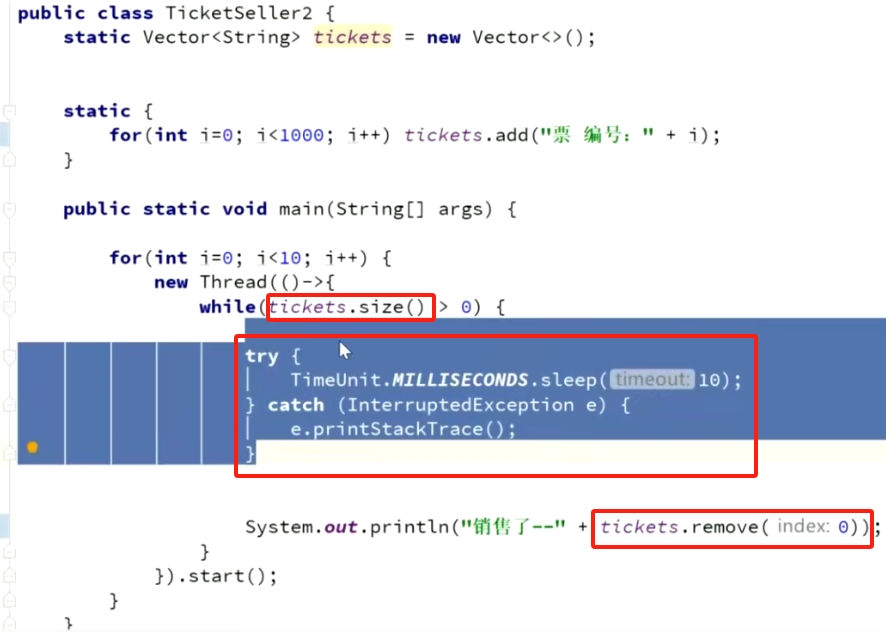
Vector发展历程 高并发问题
解决1-sychronize 同步块包围size和remove操作
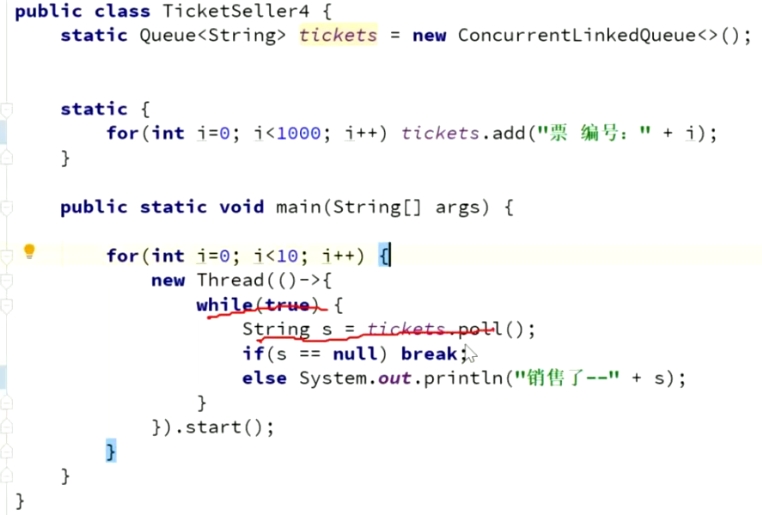
解决2-ConcurrentLinkedQueue
总结 Vector使用snychronized、ConcurrentLinkedQueue使用CAS
ConcurrentHashmap/ConcurrentSkipListMap map中有hashmap无序,treemap有序的区别但线程安全的类却使用ConcurrentSkipListMap而没有实现ConcurrentTreeMap,因为ConcurrentHashmap使用CAS操作,用在树结构时实现复杂,故而使用跳表代替
CopyOnWriteList 适用于读很多写少的情况,对比SynchronizedList
Queue LinkedQueue ConcurrentLinkedQueue peek 取但不删除
BlockingQueue LinkedBlockingQueue put,take 如果队列已满则阻塞等待,直到可以添加或获取
ArrayBlockingQueue 有上限,LinkedBlockingQueue无上限
DelayQueue 按紧迫程度排序
SynchronousQueue 容量为0,add操作会抛出异常
LinkedTransferQueue 可以add元素
在队列中已有元素的情况下,调用 transfer 方法,可以确保队列中被传递元素之前的所有元素都能被处理。
PriorityQueue 二叉树,堆排序
List Queue比较 BlockingQueue提供了很多线程友好的api,如
并发编程三大特性 线程池 自定义线程池
Executor runnable 相比Runnable,有返回值
Future 获取结果
FutureTask 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static void testFutureTask() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { FutureTask<String> ft = new FutureTask(() -> { System.out.println("ft"); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); return "1"; }); new Thread(ft).start(); System.out.println(ft.get()); }
CompletableFuture 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 CompletableFuture<String> c1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("sleep 1"); return "1"; }); CompletableFuture<String> c3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("sleep 3"); return "3"; }); Supplier<String> stringSupplier = () -> { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("sleep 2"); return "2"; }; CompletableFuture<String> c2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(stringSupplier); CompletableFuture.allOf(c1, c2, c3).join(); CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(stringSupplier) .thenApply(String::valueOf) .thenApply(s -> "str" + s) .thenAccept(System.out::println); System.in.read();
ThreadPoolExecutor参数说明 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2//核心线程(不释放) , 4//最大线程数 ,60//空闲时间 ,TimeUnit.SECONDS//空闲时间(单位) ,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4)//任务队列,使用不同的BlockingQueue会产生不同的线程池,linkedBlockingQueue 最多Integer.Max个任务, ,Executors.defaultThreadFactory()//指定了name group等 ,new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()//拒绝策略,2个核心线程在忙,后续线程进入任务队列,任务队列满,创建新线程执行任务,线程数达到最大仍然忙不过来,执行拒绝策略 //1. Abort 异常 //2.Discard 扔掉,不抛异常 //3.DiscardOldest 扔掉排队时间最久的任务,应用场景:旧数据相对来说没有意义了 //4.CallerRunsPolicy 在调用executor线程中执行,若此线程已终止则Discard //一般会自定义处理策略,需要保存消息,尤其是对于订单等请求需要记录请求日志;大量任务不能被消费处理时,需要机器扩容 );
ThreadPoolExecutor线程池 newSingleThreadExecutor Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor()
newCachedThreadPool 线程池中的线程数有弹性
newFixedThreadPool 适用场景 流量平稳,不会出现高峰(不回因为线程不足任务堆积)
newScheduledThreadPool 适用场景:定时任务
ThreadPoolExecutor源码 常用变量解释 ctl ctl int型 前三位表示线程池状态 后29位表示线程数
线程池5种状态 RUNNINg 运行
其他方法
提交任务的方法Execute 核心线程处理 -> 核心线程队列 -> 非核心线程处理 -> 拒绝策略
获取线程池状态
有空闲的core线程则交予其处理
无空闲core线程放入core线程任务队列
core线程任务队列已满,添加新非core线程执行此任务
若无法添加非core线程执行任务,执行拒绝策略
AddWorker 1.线程数+1
Worker类(线程池任务单元) 1 2 3 private final class Worker extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer implements Runnable
继承自AQS、Runnable,本身是锁且可执行
ForkJoinPool 大任务切分成小任务
ForkJoinTask RecursiveAction RecursiveAction extends ForkJoinTask
WorkStealingPool Executors.newWorkStealingPool()返回的是ForkJoinPool
JMH
官方示例 https://hg.openjdk.org/code-tools/jmh/file/2be2df7dbaf8/jmh-samples/src/main/java/org/openjdk/jmh/samples/
什么是JMH Java Microbenchmark Harness
创建JMH测试 引入依赖 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <!--jmh 基准测试 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId> <artifactId>jmh-core</artifactId> <version>1.23</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId> <artifactId>jmh-generator-annprocess</artifactId> <version>1.23</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>
安装插件
配置
JMH中的基本概念 warmup 预热 @Warmup(iterations = 3,time = 5,timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS)
Measurement 测试
Fork 创建多进程测试
Threads 创建多线程测试
BenchmarkMode 测试模式
Throughput吞吐量 点位时间调用次数;
AverageTime:平均耗时,指的是每次执行的平均时间。如果这个值很小不好辨认,可以把统计的单位时间调小一点;
SampleTime: 随机 取样 ;
SingleShotTime:执行一次,测试启动;
All:所有的指标,都算一遍,
Disruptor 用于替代并发线程间数据交换的环形队列的、基本无锁(使用cas)的(只有部分等待策略存在)、高性能的线程间通讯框架
特点
环形数组:覆盖旧的数据,降低GC频率,且数组对于处理器缓存机制更友好
无锁(使用CAS),高性能,单机高并发
位运算确定index(比取模快)
数组实现队列,ConcurrentLinkedQueue是链表实现,且
RingBuffer 只记录下一个有效元素位置(sequence),数组实现,没有首尾指针(ConcurrentLinkedQueue添加删除时要加锁)。
长度设为2的n次幂,利于二进制计算,例如:第12个元素存放位置12%8=12&(8-1) pos=num&(size-1)
buffer大小取决于:消息大小,内存大小
基本用法 普通写法 lamda表达式 指定生产者线程模式
Single(确定生产者只有一个线程时使用)
Multi
等待策略 Block
指定多消费者 多消费者,对应多线程
异常处理 java线程池体系 面试题 1 实现一个容器,提供两个方法,add,size
wait/notify实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public class q1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyContainer myContainer = new MyContainer(); Object locker = new Object(); Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { synchronized (locker) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { myContainer.add(i); System.out.println("size:" + myContainer.size()); if (myContainer.size() == 5) { try { System.out.println("t1 notify"); locker.notify(); System.out.println("t1 wait"); locker.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } }); Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { synchronized (locker) { try { System.out.println("t2 wait"); locker.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } if (myContainer.size() == 5) { System.out.println("t2 notify"); locker.notify(); } System.out.println("t2 end"); } }); t2.start(); Thread.sleep(100); t1.start(); } } class MyContainer { List<Integer> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()); public void add(Integer i) { list.add(i); } public int size() { return list.size(); } }
CountDownLatch实现 LockSupport实现 2 为什么说AQS是CAS+volatile 写一个固定容量的同步容器,有put和get方法,以及getCount方法,能支持两个生产者线程以及10个消费者线程
问题
ThreadGroup? new Thread(ThreadGroup)
synchronized reentranlock 锁升级?
如何确定站点的并发量
wait notify
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Object locker = new Thread(); new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("t lock"); synchronized (locker) { try { System.out.println("t will sleep 5s"); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } try { System.out.println("t sleep end ,wait"); locker.wait(); System.out.println("t wait end"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }).start(); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); System.out.println("main lock"); synchronized (locker) { System.out.println("main notify"); locker.notify(); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("main lock end"); } }
await signal
并发/并行
JDK中没有ConcurrentArrayQueue
DaemonThreadFactory